The Button Widget
Normal Buttons
We've almost seen all there is to see of the button widget. It's pretty simple. There is however more than one way to create a button. You can use the gtk_button_new_with_label() or gtk_button_new_with_mnemonic() to create a button with a label, use gtk_button_new_from_stock() to create a button containing the image and text from a stock item or use gtk_button_new() to create a blank button. It's then up to you to pack a label or pixmap into this new button. To do this, create a new box, and then pack your objects into this box using the usual gtk_box_pack_start(), and then use gtk_container_add() to pack the box into the button.
Here's an example of using gtk_button_new() to create a button with a image and a label in it. I've broken up the code to create a box from the rest so you can use it in your programs. There are further examples of using images later in the tutorial.
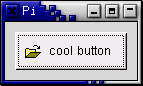
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <gtk/gtk.h>
/* Create a new hbox with an image and a label packed into it
* and return the box. */
static GtkWidget *xpm_label_box( gchar *xpm_filename,
gchar *label_text )
{
GtkWidget *box;
GtkWidget *label;
GtkWidget *image;
/* Create box for image and label */
box = gtk_hbox_new (FALSE, 0);
gtk_container_set_border_width (GTK_CONTAINER (box), 2);
/* Now on to the image stuff */
image = gtk_image_new_from_file (xpm_filename);
/* Create a label for the button */
label = gtk_label_new (label_text);
/* Pack the image and label into the box */
gtk_box_pack_start (GTK_BOX (box), image, FALSE, FALSE, 3);
gtk_box_pack_start (GTK_BOX (box), label, FALSE, FALSE, 3);
gtk_widget_show (image);
gtk_widget_show (label);
return box;
}
/* Our usual callback function */
static void callback( GtkWidget *widget,
gpointer data )
{
g_print ("Hello again - %s was pressed\n", (char *) data);
}
int main( int argc,
char *argv[] )
{
/* GtkWidget is the storage type for widgets */
GtkWidget *window;
GtkWidget *button;
GtkWidget *box;
gtk_init (&argc, &argv);
/* Create a new window */
window = gtk_window_new (GTK_WINDOW_TOPLEVEL);
gtk_window_set_title (GTK_WINDOW (window), "Pixmap'd Buttons!");
/* It's a good idea to do this for all windows. */
g_signal_connect (G_OBJECT (window), "destroy",
G_CALLBACK (gtk_main_quit), NULL);
g_signal_connect (G_OBJECT (window), "delete_event",
G_CALLBACK (gtk_main_quit), NULL);
/* Sets the border width of the window. */
gtk_container_set_border_width (GTK_CONTAINER (window), 10);
/* Create a new button */
button = gtk_button_new ();
/* Connect the "clicked" signal of the button to our callback */
g_signal_connect (G_OBJECT (button), "clicked",
G_CALLBACK (callback), (gpointer) "cool button");
/* This calls our box creating function */
box = xpm_label_box ("info.xpm", "cool button");
/* Pack and show all our widgets */
gtk_widget_show (box);
gtk_container_add (GTK_CONTAINER (button), box);
gtk_widget_show (button);
gtk_container_add (GTK_CONTAINER (window), button);
gtk_widget_show (window);
/* Rest in gtk_main and wait for the fun to begin! */
gtk_main ();
return 0;
} |
The xpm_label_box() function could be used to pack images and labels into any widget that can be a container.
The Button widget has the following signals:
pressed - emitted when pointer button is pressed within Button widget
released - emitted when pointer button is released within Button widget
clicked - emitted when pointer button is pressed and then released within Button widget
enter - emitted when pointer enters Button widget
leave - emitted when pointer leaves Button widget